Cultural Dimensions of Leadership
April 3, 2025
 Cultural Dimensions of Leadership
Cultural Dimensions of Leadership
Introduction Leadership in organizations is dictated and determined according to a variety of reasons and factors including personality, cultural, and country and regional aspects. Among the various factors, the cultural dimension of leadership is often not highlighted as it is taken as a given. However, with globalization and the advent of tighter integration and interconnectedness,…
 Continuum of Leadership Behaviour
Continuum of Leadership Behaviour
The leadership continuum was originally written in 1958 by Tannenbaum and Schmidt and was later updated in the year 1973. Their work suggests a continuum of possible leadership behavior available to a manager and along which many leadership styles may be placed. The continuum presents a range of action related to the degree of authority…
 The Challenge for Contemporary Leaders is to Restore Trust and Faith in Institutions
The Challenge for Contemporary Leaders is to Restore Trust and Faith in Institutions
Loss of Trust and Faith and the Rise of Populists Public trust and faith in institutions is at an all time low. Starting with the Global Financial Crisis of 2008 in the United States and then the Sovereign Debt Crisis in Europe in 2009, including the Brexit vote in the United Kingdom, and the election…
The treatment of task orientation and people orientation as two independent dimensions was a major step in leadership studies.
Many of the leadership studies conducted in the 1950s at the University of Michigan and the Ohio State University focused on these two dimensions.
Building on the work of the researchers at these Universities, Robert Blake and Jane Mouton (1960s) proposed a graphic portrayal of leadership styles through a managerial grid (sometimes called leadership grid).
The grid depicted two dimensions of leader behavior, concern for people (accommodating people’s needs and giving them priority) on y-axis and concern for production (keeping tight schedules) on x-axis, with each dimension ranging from low (1) to high (9), thus creating 81 different positions in which the leader’s style may fall. (See figure 1).
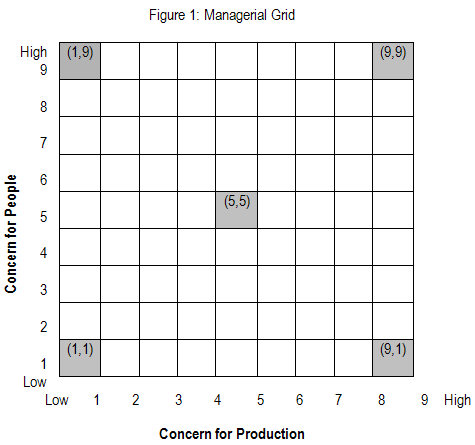
The five resulting leadership styles are as follows:
The leader has low concern for employee satisfaction and work deadlines and as a result disharmony and disorganization prevail within the organization. The leaders are termed ineffective wherein their action is merely aimed at preserving job and seniority.
The employees’ needs are not taken care of and they are simply a means to an end. The leader believes that efficiency can result only through proper organization of work systems and through elimination of people wherever possible.
Such a style can definitely increase the output of organization in short run but due to the strict policies and procedures, high labour turnover is inevitable.
The leader does not push the boundaries of achievement resulting in average performance for organization. Here neither employee nor production needs are fully met.
The leader feels that such a treatment with employees will lead to self-motivation and will find people working hard on their own. However, a low focus on tasks can hamper production and lead to questionable results.
The leader feels that empowerment, commitment, trust, and respect are the key elements in creating a team atmosphere which will automatically result in high employee satisfaction and production.
The Managerial or Leadership Grid is used to help managers analyze their own leadership styles through a technique known as grid training. This is done by administering a questionnaire that helps managers identify how they stand with respect to their concern for production and people.
The training is aimed at basically helping leaders reach to the ideal state of 9, 9.
The model ignores the importance of internal and external limits, matter and scenario. Also, there are some more aspects of leadership that can be covered but are not.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *