Principles of Scientific Management
April 3, 2025
 Principles of Scientific Management
Principles of Scientific Management
Development of Science for each part of men’s job (replacement of rule of thumb) This principle suggests that work assigned to any employee should be observed, analyzed with respect to each and every element and part and time involved in it. This means replacement of odd rule of thumb by the use of method of…
 Scientific Management by Taylor
Scientific Management by Taylor
Fredrick Winslow Taylor ( March 20, 1856 – March 21, 1915) commonly known as ’Father of Scientific Management’ started his career as an operator and rose to the position of chief engineer. He conducted various experiments during this process which forms the basis of scientific management. It implies application of scientific principles for studying identifying…
 Techniques of Scientific Management
Techniques of Scientific Management
Time Study It is a technique which enables the manager to ascertain standard time taken for performing a specified job. Every job or every part of it is studied in detail. This technique is based on the study of an average worker having reasonable skill and ability. Average worker is selected and assigned the job…
The term “Levels of Management” refers to a line of demarcation between various managerial positions in an organization. The number of levels in management increases when the size of the business and work force increases and vice versa.
The level of management determines a chain of command, the amount of authority status enjoyed by any managerial position.
The levels of management can be classified in three broad categories:
Managers at all these levels perform different functions. The role of managers at all the three levels is discussed below:
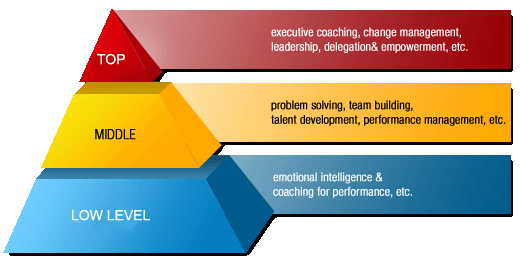
It consists of board of directors, chief executive or managing director.
The top management is the ultimate source of authority and it manages goals and policies for an enterprise. It devotes more time on planning and coordinating functions.
The role of the top management can be summarized as follows -
The branch managers and departmental managers constitute middle level. They are responsible to the top management for the functioning of their department. They devote more time to organizational and directional functions.
In small organization, there is only one layer of middle level of management but in big enterprises, there may be senior and junior middle level management. Their role can be emphasized as -
Lower level is also known as supervisory/operative level of management. It consists of supervisors, foreman, section officers, superintendent etc.
According to R.C. Davis, “Supervisory management refers to those executives whose work has to be largely with personal oversight and direction of operative employees”.
In other words, they are concerned with direction and controlling function of management. Their activities include -
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *