Cutting Costs Strategically
April 3, 2025
 Cutting Costs Strategically
Cutting Costs Strategically
The business environment today has become extremely competitive. Companies are not only facing competition from their local competitors but also from global ones. Different economic and geopolitical factors make global supply chains necessary. The problem with having global supply chains is that operations become broad and complex. It is much easier to manage operations located…
 What is Competitive Advantage in the Field of Strategic Management?
What is Competitive Advantage in the Field of Strategic Management?
What is Competitive Advantage? It is a truism that strategic management is all about gaining and maintaining competitive advantage. The term can be defined to mean “anything that a firm does especially well when compared with rival firms”. Note the emphasis on comparison with rival firms as competitive advantage is all about how best to…
 Competitor Analysis – Meaning, Objectives and Significance
Competitor Analysis – Meaning, Objectives and Significance
Organizations must operate within a competitive industry environment. They do not exist in vacuum. Analyzing organization’s competitors helps an organization to discover its weaknesses, to identify opportunities for and threats to the organization from the industrial environment. While formulating an organization’s strategy, managers must consider the strategies of organization’s competitors. Competitor analysis is a driver…
Michael Porter (Harvard Business School Management Researcher) designed various vital frameworks for developing an organization’s strategy. One of the most renowned among managers making strategic decisions is the five competitive forces model that determines industry structure. According to Porter, the nature of competition in any industry is personified in the following five forces:
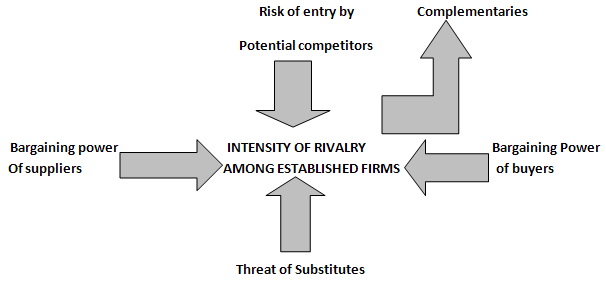
The five forces mentioned above are very significant from point of view of strategy formulation. The potential of these forces differs from industry to industry. These forces jointly determine the profitability of industry because they shape the prices which can be charged, the costs which can be borne, and the investment required to compete in the industry. Before making strategic decisions, the managers should use the five forces framework to determine the competitive structure of industry.
Let’s discuss the five factors of Porter’s model in detail:
Bargaining power of buyers refer to the potential of buyers to bargain down the prices charged by the firms in the industry or to increase the firms cost in the industry by demanding better quality and service of product.
Strong buyers can extract profits out of an industry by lowering the prices and increasing the costs. They purchase in large quantities. They have full information about the product and the market. They emphasize upon quality products. They pose credible threat of backward integration. In this way, they are regarded as a threat.
Bargaining power of the suppliers refer to the potential of the suppliers to increase the prices of inputs( labour, raw materials, services, etc) or the costs of industry in other ways.
Strong suppliers can extract profits out of an industry by increasing costs of firms in the industry. Suppliers products have a few substitutes. Strong suppliers’ products are unique. They have high switching cost. Their product is an important input to buyer’s product. They pose credible threat of forward integration. Buyers are not significant to strong suppliers. In this way, they are regarded as a threat.
Lesser the number of close substitutes a product has, greater is the opportunity for the firms in industry to raise their product prices and earn greater profits (other things being equal).
The power of Porter’s five forces varies from industry to industry. Whatever be the industry, these five forces influence the profitability as they affect the prices, the costs, and the capital investment essential for survival and competition in industry.
This five forces model also help in making strategic decisions as it is used by the managers to determine industry’s competitive structure.
Porter ignored, however, a sixth significant factor- complementaries. This term refers to the reliance that develops between the companies whose products work is in combination with each other. Strong complementors might have a strong positive effect on the industry.
Also, the five forces model overlooks the role of innovation as well as the significance of individual firm differences. It presents a stagnant view of competition.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *