Creating Sustainable Change – How to create and sustain change?
April 3, 2025
 Creating Sustainable Change – How to create and sustain change?
Creating Sustainable Change – How to create and sustain change?
Who doesn’t like change and who doesn’t want to change? These are certainly truisms in the 21st century landscape where businesses proclaim their commitment to change and exhort their employees to “Be the change you want to see”. However, having a vision and mission statement that commits to change is different from actualizing the change.…
 Why Some Organizations are Better at Driving Change ?
Why Some Organizations are Better at Driving Change ?
We live in a world where increasing complexity is the order of the day and the business landscape is characterized by a rapid turnover of companies which find themselves dethroned from their position because of outmoded thinking or anachronistic strategies. For instance, Nokia and RIM (the maker of Blackberry) were at the top of the…
 Contingency Model of Change Management: Dunphy and Stace’s Model of Change
Contingency Model of Change Management: Dunphy and Stace’s Model of Change
The contingency model is an extended version of Lewin’s three step in which Dunphy and Stace (1988, 1992 and 1993), explained the process of change from the transformational organization perspective. Dunphy and Stace (1993), put forth a situational or contingency model of change, which emphasized on the fact that organizations should vary their change strategies…
This model of change is one of the unique models of change as propounded by Cynthia Scott Dennis Jaffe in their article ‘Survive and Thrive in Times of Change’.
The model derives its inspiration from the work of Elisabeth Kubler-Ross, in which she highlighted through her research the ways in which people coped with tragedies, grief or sorrow and based on her investigation she identified five stages of grief:
In a similar manner, Scott and Jaffe described the entire psychological process and how individuals respond to change.
The key highlights of this model havebeen given below:
As per Scott and Jaffe, we all transition through 4 stages of change:
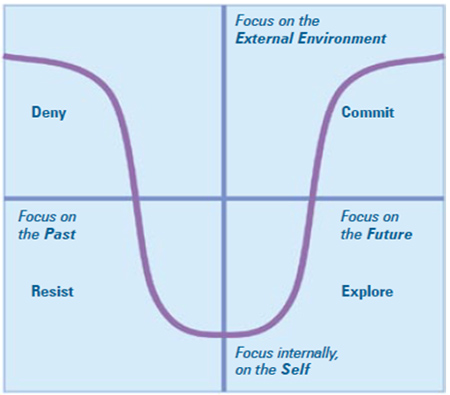
The resistance is usually exhibited through emotional upsurges in the form of anger, frustration, anxiety, fear of the unknown and sometimes voice it out by opposing the change vociferously.
It is during this stage when the organization witnesses a loss in productivity as well as the overall stability in the business environment due to this resistance.
This stage is very sensitive and tentative as for any wrong step taken people may once again revert to the resistance stage of change.
It is very important that commitment towards the change can be established by backing it up with appropriate recognitions and clearly defining the Roles and Accountabilities of the employees.
The model of Change as propounded by Scott and Jaffe is regarded as a predictive model which is far from the reality. But the model can be considered as a vital framework for understanding the process of change and it provides crucial insights on how one can manage change successfully by minimizing the resistance.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *